以长广溪国家城市湿地公园一期景观设计为例
The Application of Ecological Water Filtration Systems in Urban Wetland Park Design
Taking the Landscape Design of Chang Guang Xi River National Urban Wetland Park as an Example
吕娜 王小璘
LV Na WANG Xiao-lin
摘要:以长广溪国家城市湿地公园一期示范段景观设计为例,通过该项目应用的3种生态水质净化技术——重力过滤系统,廉布过滤系统,沉淀溢流过滤系统——的设计、施工、及运行一年后获得的水质监测数据、向公众开放五年来的运行和维护状况,进行总结分析。首先就建设实施造价、净化效果、后期维护等方面,分析每种水质净化技术的特性以及优劣势;其次,针对每种技术的特性和要求,探索其与景观设计有机融合的方法;最后,总结3种生态水质净化方法在景观设计应用中的利弊,为今后类似的景观设计项目提供技术检测参数和景观生态设计方法参考。
关键词:风景园林;湿地公园;园林工程;生态水质净化;雨水管理
Abstract: Taking the landscape design of Chang Guang Xi River National Urban Wetland Park as an example, this paper introduces three ecological water filtration methods-gravity filtration system,flow-balancing filtration system and settlement-overflow filtration system-and analyzes the design, construction, the one-year water quality monitoring data and the 5-year operating and maintaining conditions after open-up of the mentioned methods. Based on the construction implementation cost, filtration effects and maintenance conditions, this paper first gives an analysis of the features, advantages and disadvantages of each method. It then explores the possibilities of the integration of the methods and landscape design according to the analyzed features and requirements, followed by a conclusion of the advantages and disadvantages of the application of each filtration method in landscape design. Technical detection parameters and landscape ecological design references to similar landscape design projects will be given at the end of this paper.
Key words: Landscape Architecture; Wetland Park; Landscape Engineering; Ecological Water Filtration; Storm Water Management
生态景观设计从本质上说是对土地和户外空间的生态设计,其核心是生态原理,从更深层意义来说,是对人类生态系统的设计,是最大限度地借助于自然力的最少设计,反映了人与自然合作与友爱的关系,反映了设计者对自然和社会的责任,在当今生态问题备受关注的背景下,生态景观设计势在必行[1]。如何将实践证明有效的生态技术融合于景观设计,亦是一个非常值得探讨的课题。本文结合笔者的案例实践——长广溪国家城市湿地公园一期景观设计,侧重探索景观设计的生态性中,对雨水的回收和利用以及运用生态原理净化景观水体水质、修复和重建湿地生态系统的实践过程,并追踪这些生态设计要素在实际建成运作中的效果,以期就生态水质净化技术同景观设计有机融合的方法研究方面,为今后的景观设计案例提供借鉴。
1 长广溪国家城市湿地公园项目概况
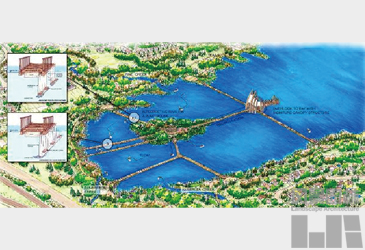
长广溪地处无锡太湖新城范围,呈南北走向,连接五蠡湖和太湖,全长约10km。长广溪国家城市湿地公园规划范围900hm2,沿长广溪两岸展开,为2005-2006年间,建设部批准挂牌的10个国家城市湿地公园中唯一进行专业水质生态净化设计的生态工程,被联合国环境署评为发展中国家湿地公园的示范项目。
自1980年代以来,长广溪流域人口密度增大,工业化进程加快,历经数次围湖造田整个区域生态环境遭受严重破坏,水体受到严重污染(表01),生态功能已严重下降,湿地自然景观进一步被破坏。2004年无锡市人民政府订下整治长广溪的目标:“将长广溪建为建立在清水走廊基础上的国家城市湿地公园”。净化水质成为本项目的首要任务,在一期景观设计中(图01),尝试引进在加拿大应用较成熟的生态水质净化系统。自2006年项目基本建成至今,公园基本实现零维护,建成运行一年后的3次检测结果也证实水质净化方法的有效性。对此一系列的水质净化方法进行回顾,根据国内的国情和针对不同的污染源选用不同的方法进行介绍,同时根据建成后的追踪水质检测分析不同净化方法的效果和针对性,在此基础上探讨净化技术同景观设计实现有机结合的方法。
(未完待续)

 《风景园林》2013第5期导读
《风景园林》2013第5期导读
Leave a Reply